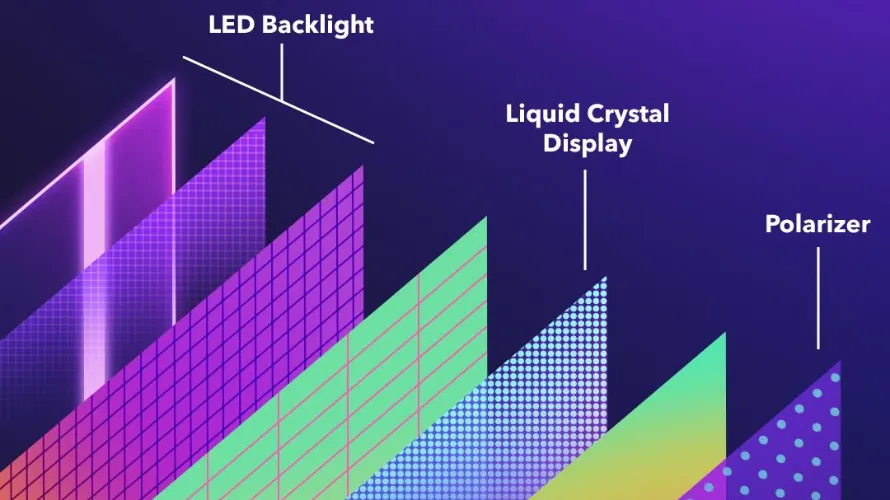
Some Basic Facts About LEDs
Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) are semiconductor devices that emit light when an electric current passes through them. They are known for their efficiency, durability, and versatility in various applications, ranging from lighting to display technologies.
Types of LED Technology
1. Surface-Mount Device (SMD) LEDs: These are the most common types of LEDs used in displays and lighting fixtures. SMD LEDs are compact and versatile, available in different sizes and configurations to suit various applications. They offer good brightness and color consistency.
2. Chip-on-Board (COB) LEDs: COB LEDs involve multiple LED chips bonded directly to a substrate to form a single module. They offer enhanced brightness, better heat dissipation, and reduced pixelation compared to SMD LEDs. COB technology is particularly advantageous in high-resolution displays and applications requiring high uniformity.
3. Mini LED: Mini LEDs are a newer technology that offers even smaller LED chips than traditional SMD LEDs. They enable higher pixel density, improved contrast ratios, and better HDR (High Dynamic Range) performance. Mini LEDs are gaining popularity in premium displays, including televisions and high-end signage.
4. OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode): Unlike traditional LEDs, OLEDs use organic materials that emit light when an electric current is applied. OLED displays offer self-emissive pixels, resulting in deep blacks, vibrant colors, and wide viewing angles. They are commonly used in high-end smartphones, TVs, and wearable devices.
The Main Advantages of LED Technology
- Energy Efficiency: LEDs consume significantly less energy than traditional lighting sources, making them environmentally friendly and cost-effective over time.
- Longevity: LED technology boasts long lifespans, often lasting tens of thousands of hours before requiring replacement. This reduces maintenance costs and downtime.
- Instantaneous Lighting: LEDs light up instantly when powered on, unlike traditional bulbs that require warm-up time. This instant-on feature is crucial for applications where quick response times are essential.
- Durability: LEDs are durable and resistant to shock, vibrations, and environmental factors. They are ideal for outdoor use and rugged environments.
- Flexibility: LED technology allows for flexible designs and applications, including curved displays, thin panels, and customizable lighting solutions.
- Color Options: LEDs can produce a wide range of colors and color temperatures, providing flexibility in creating different atmospheres and moods.
Conclusion
LED technology continues to evolve, offering diverse options to suit various lighting and display needs. From the efficiency and longevity of SMD LEDs to the high resolution and uniformity of COB LEDs and the vibrant colors of OLEDs, understanding these different technologies enables informed decisions when selecting lighting or display solutions.